


What is EAGERx
You can use EAGERx (Engine Agnostic Graph Environments for Robotics) to easily define new (Gymnasium compatible) environments with modular robot definitions.
It enables users to:
Define environments as graphs of nodes
Visualize these graph environments interactively in a GUI
Use a single graph environment both in reality and with various simulators
EAGERx explicitly addresses the differences in learning between simulation and reality, with native support for essential features such as:
Safety layers and various other state, action and time-scale abstractions
Delay simulation & domain randomization
Real-world reset routines
Synchronized parallel computation within a single environment
You can find the open-source code on Github.

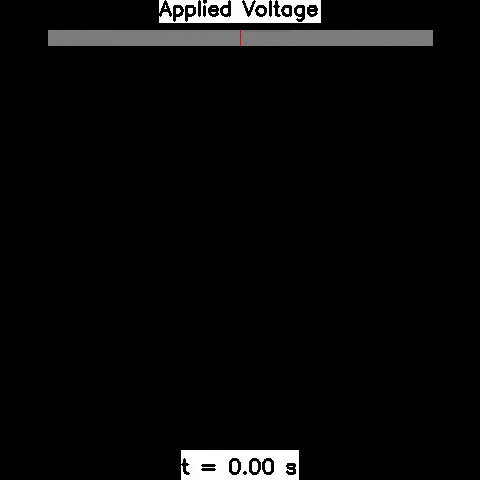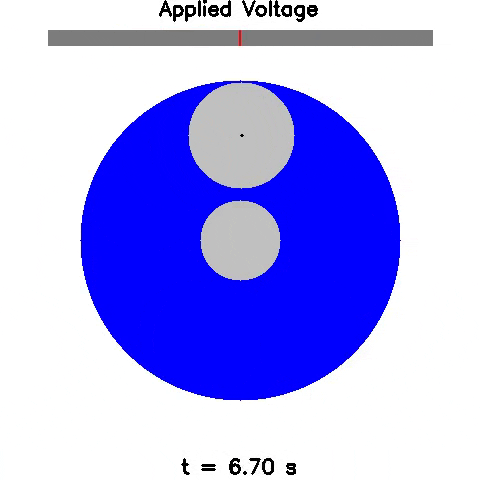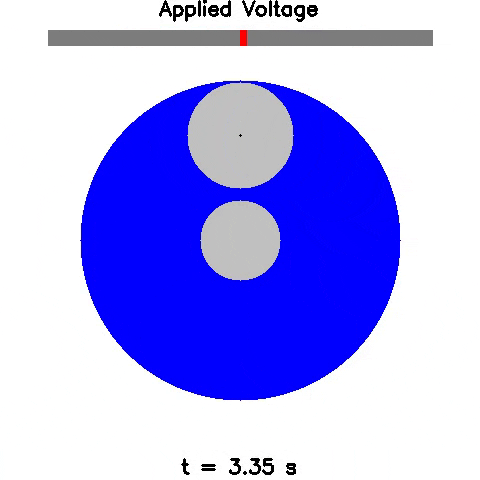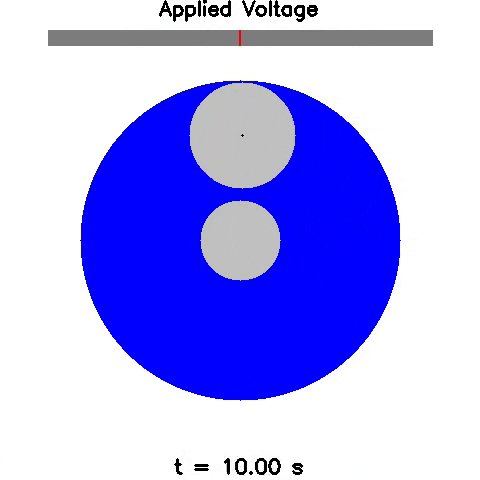

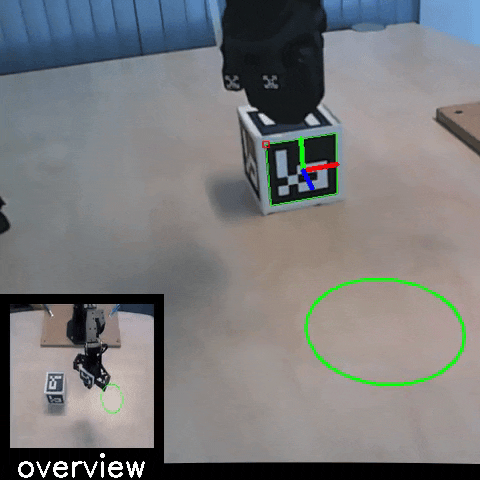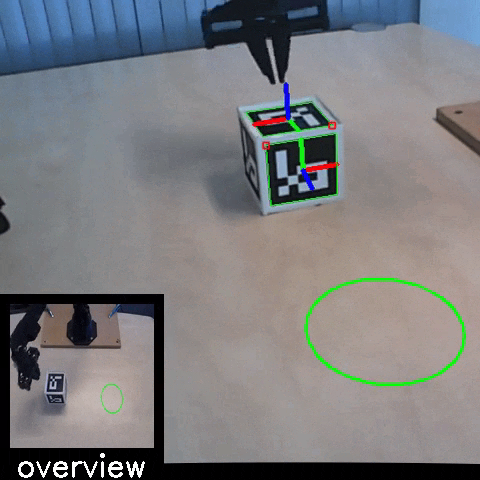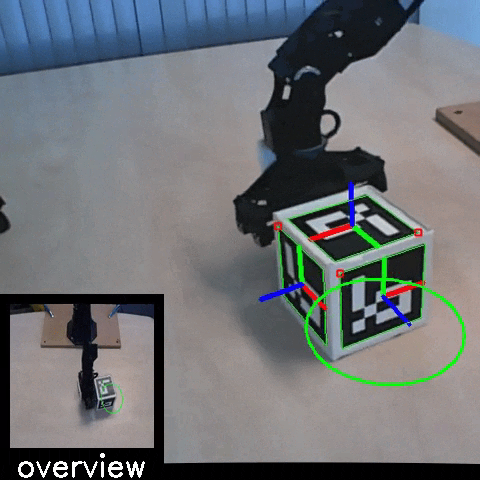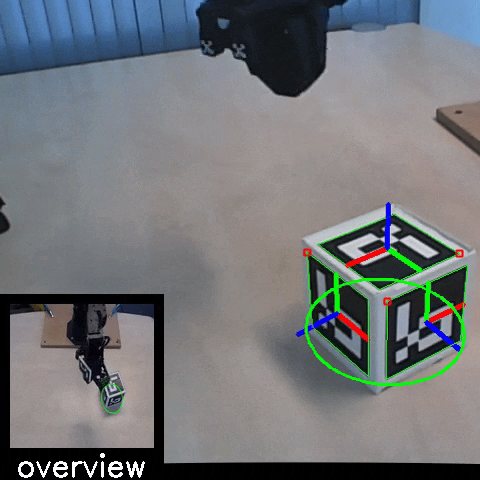
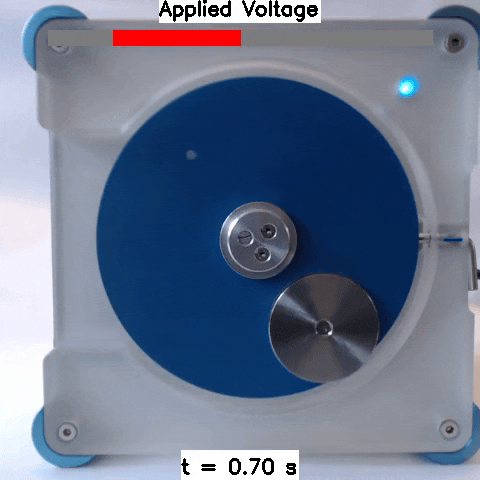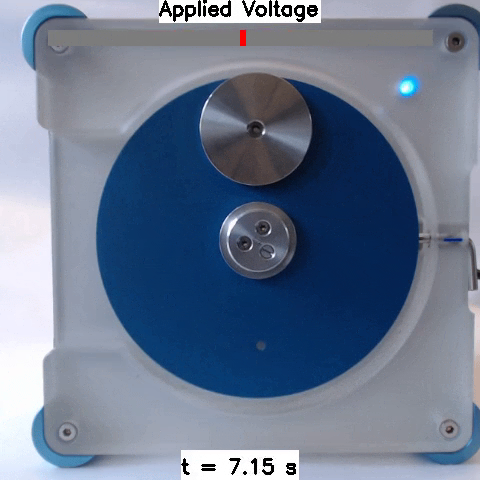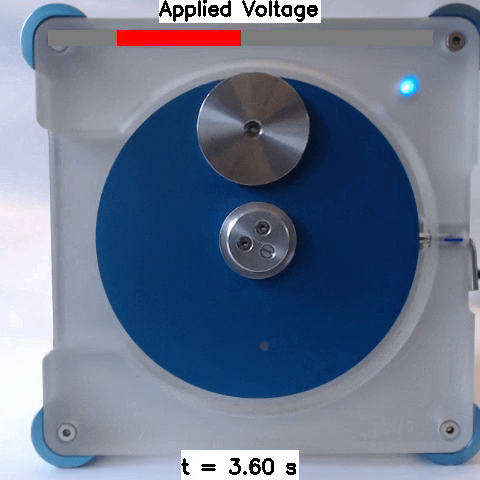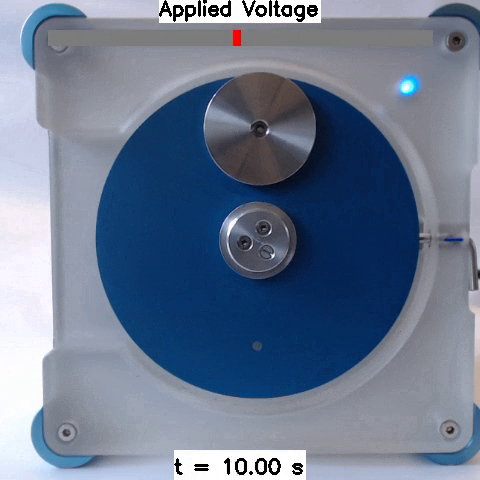

Sim2Real: Policies trained in simulation and zero-shot evaluated on real systems using EAGERx. On the left the successful transfer of a box-pushing policy is shown, in the middle for the classic pendulum swing-up problem and on the right a task involving the crazyfly drone.
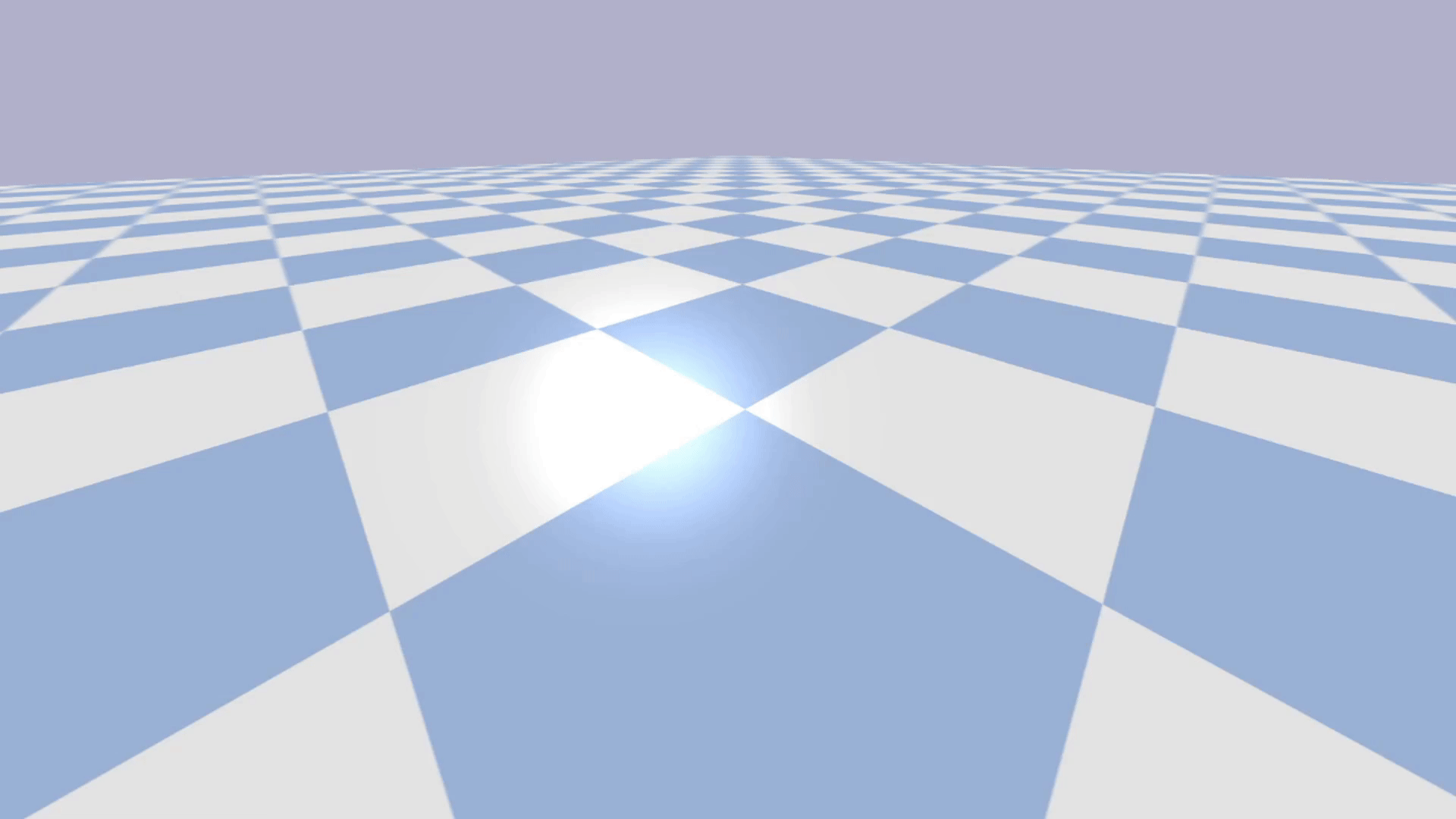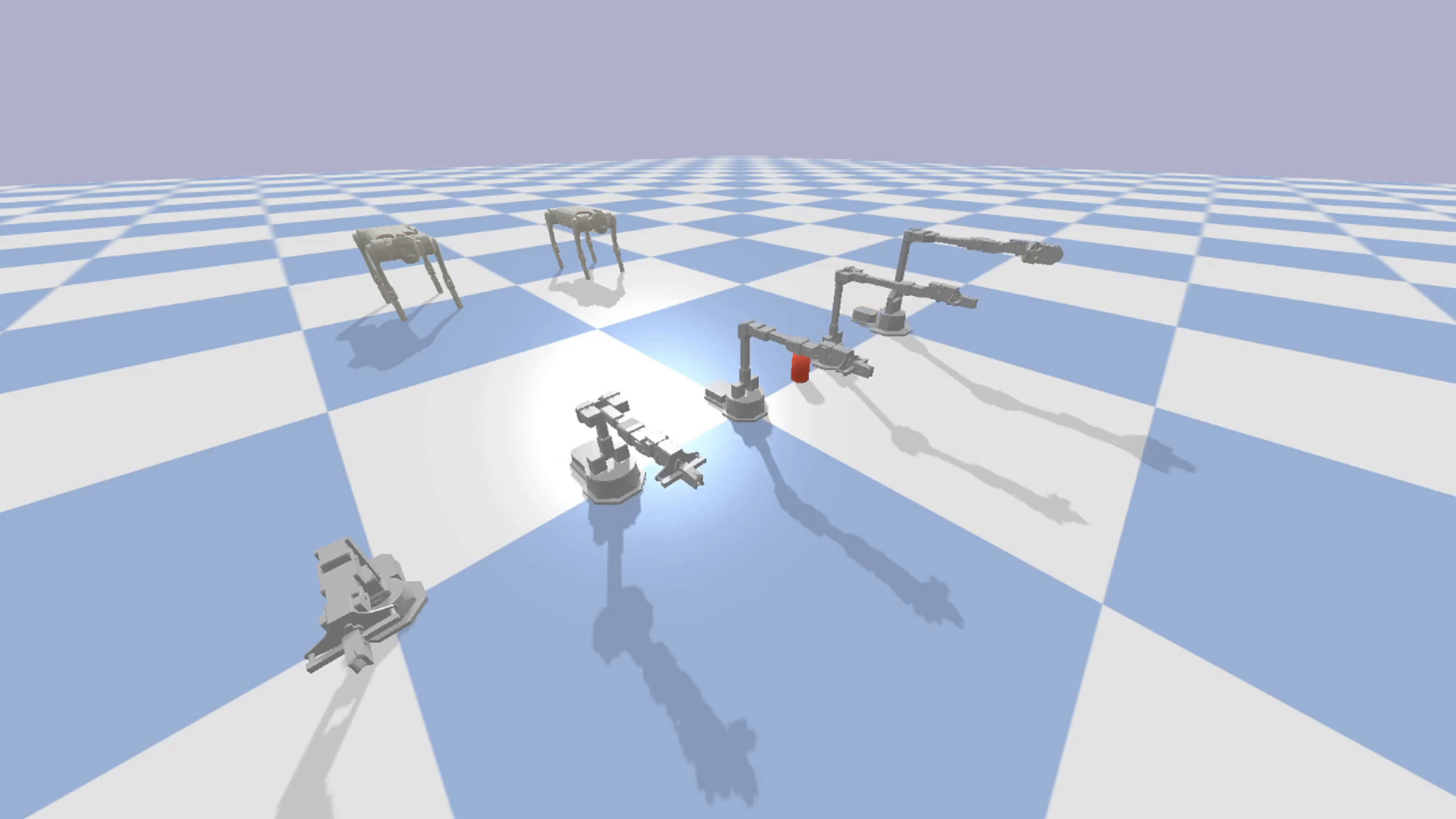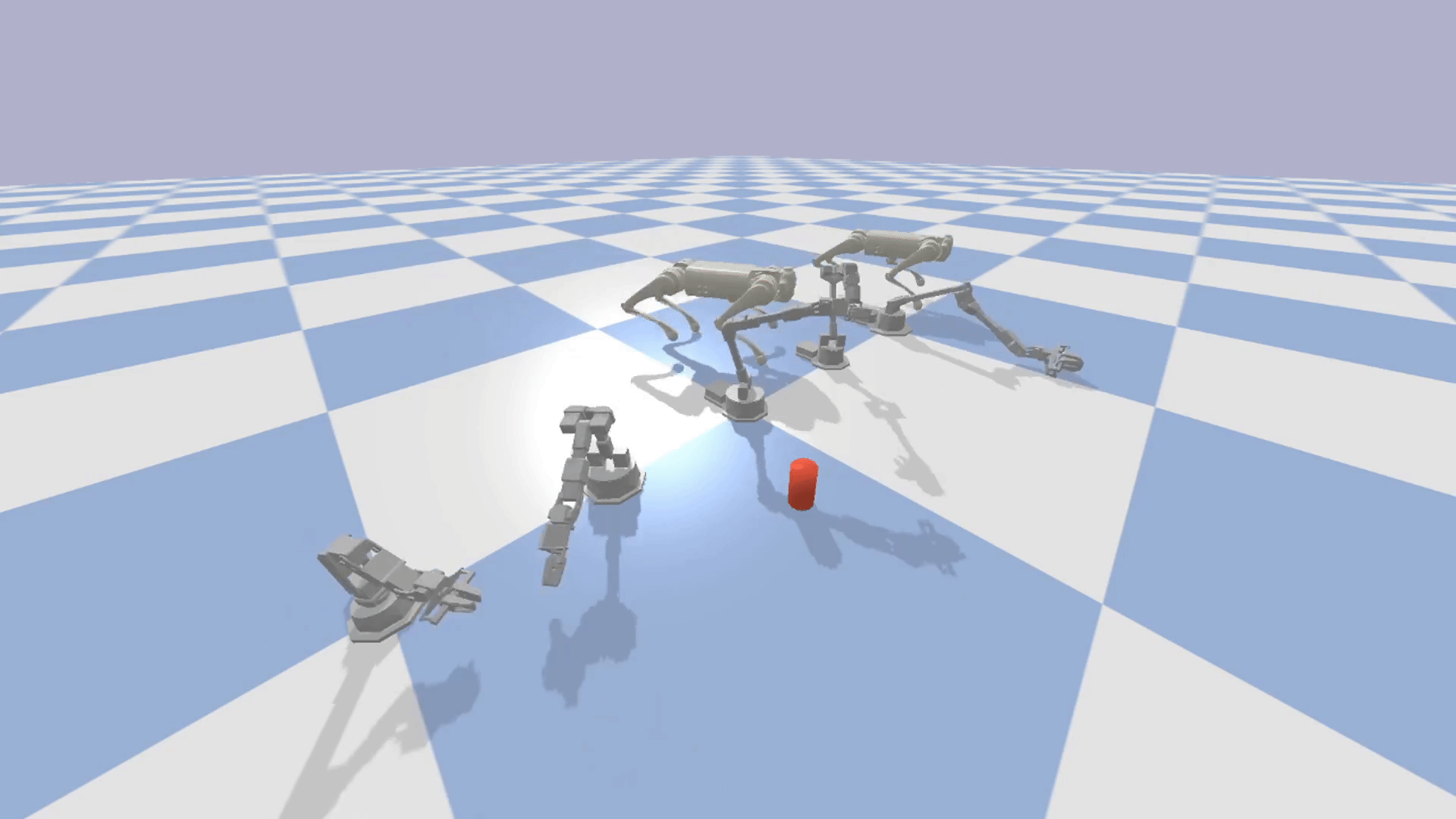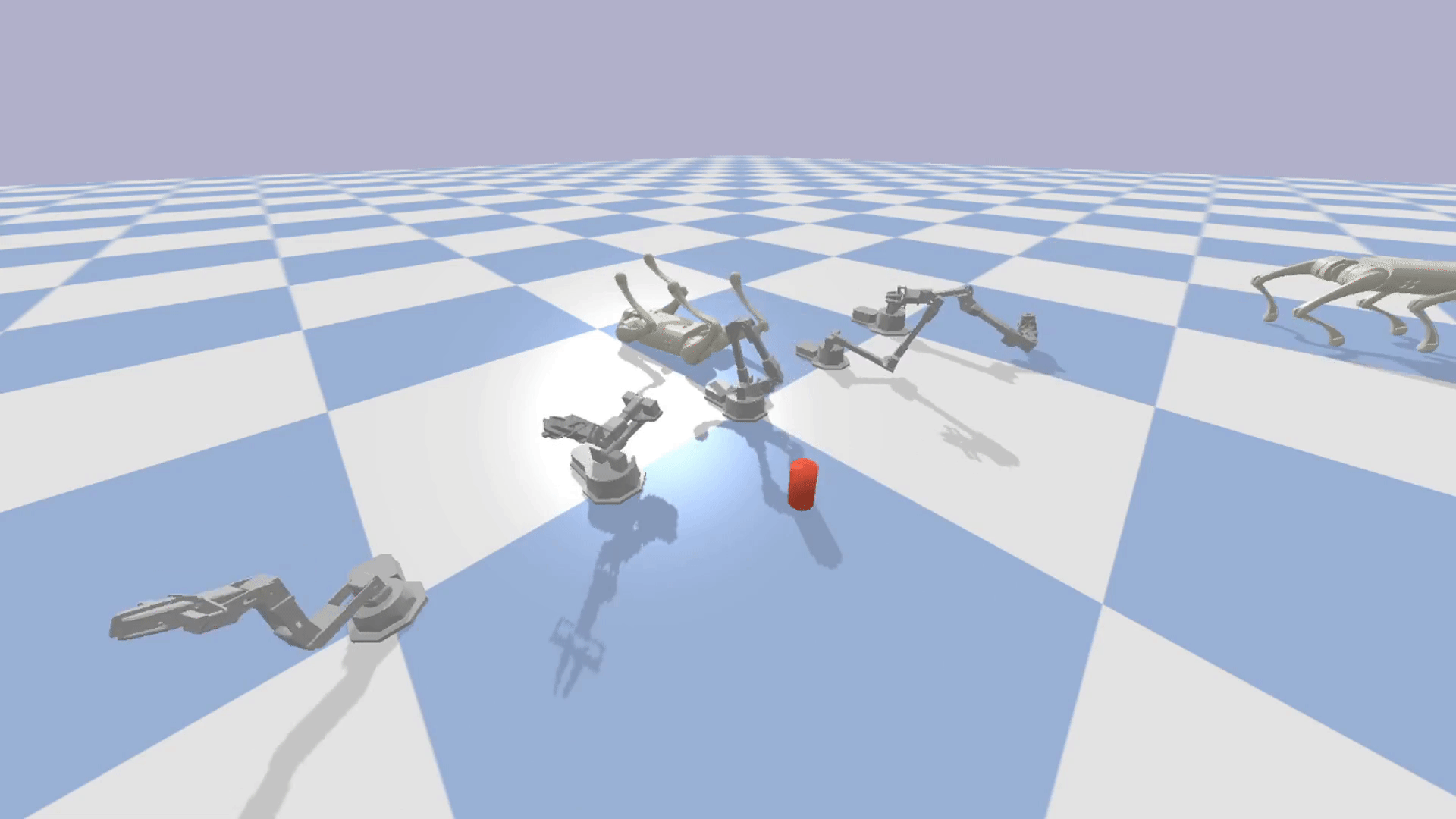
Modular: The modular design of EAGERx allows users to create complex environments easily through composition.
GUI: Users can visualize their graph environment. Here we visualize the graph environment that we built in this tutorial. See the documentation for more information.
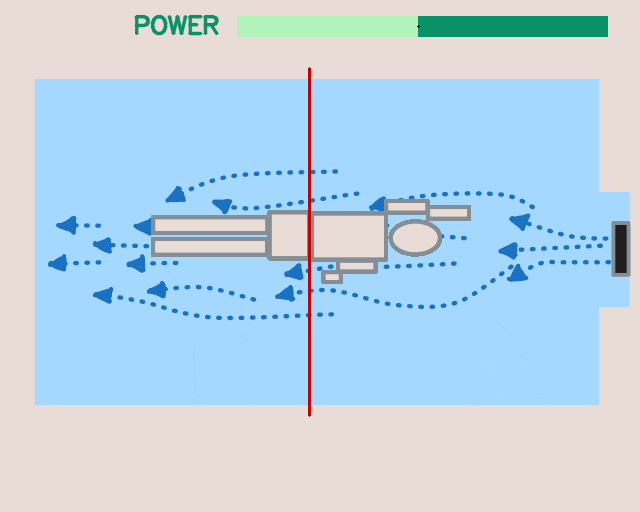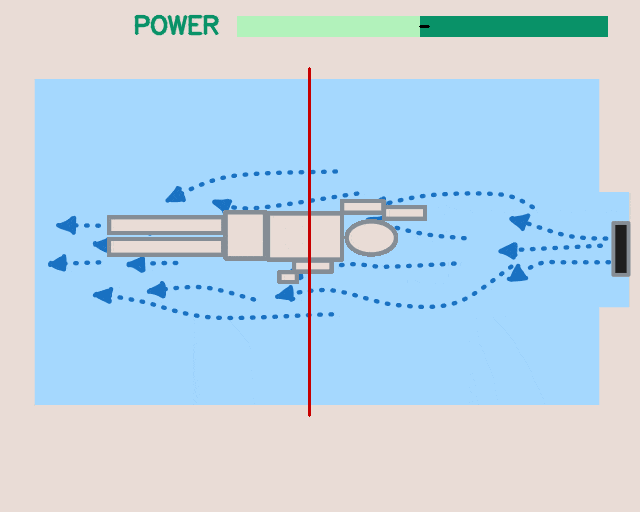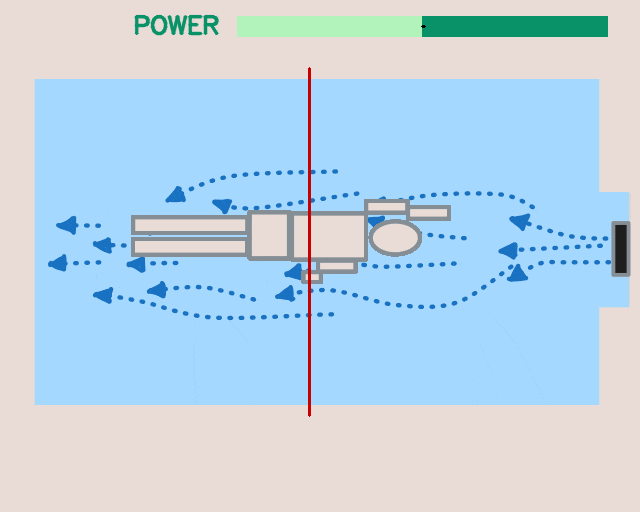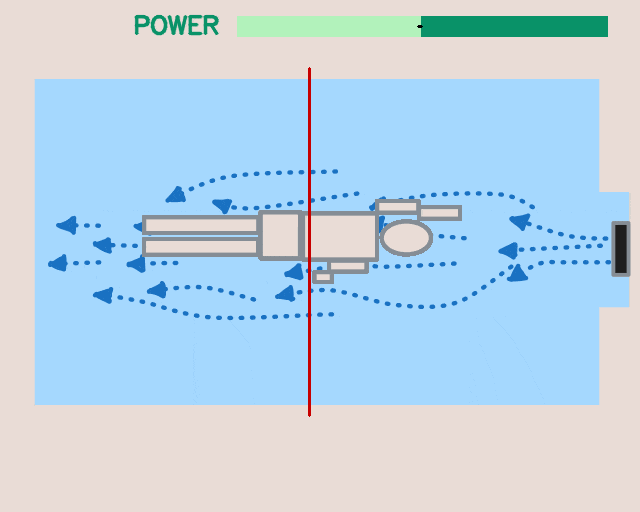
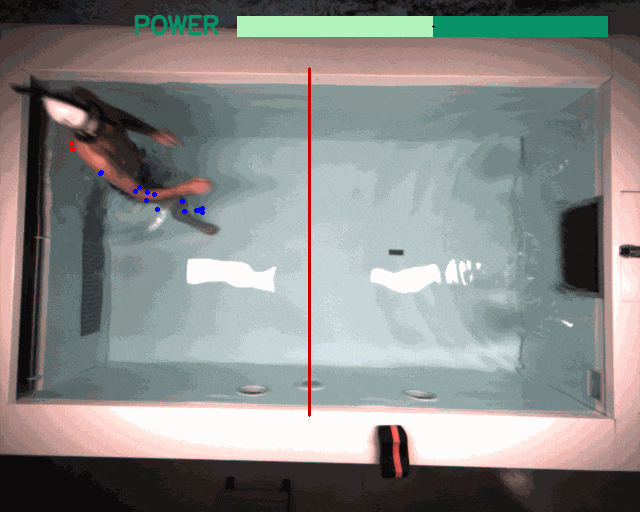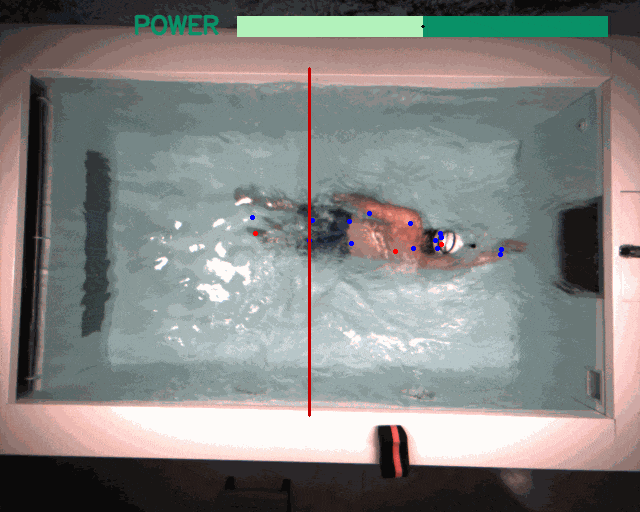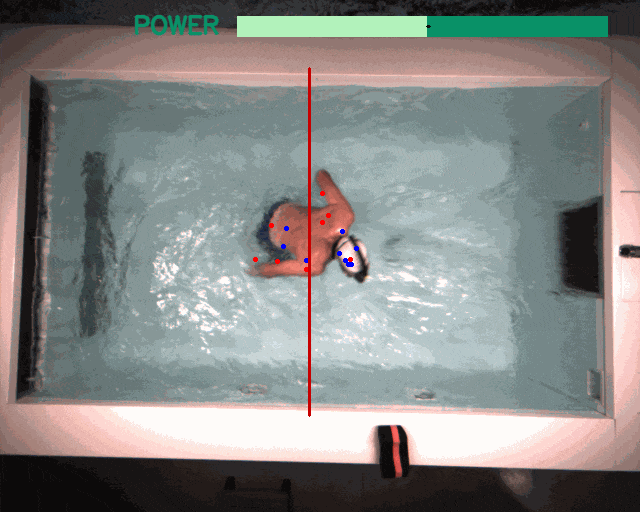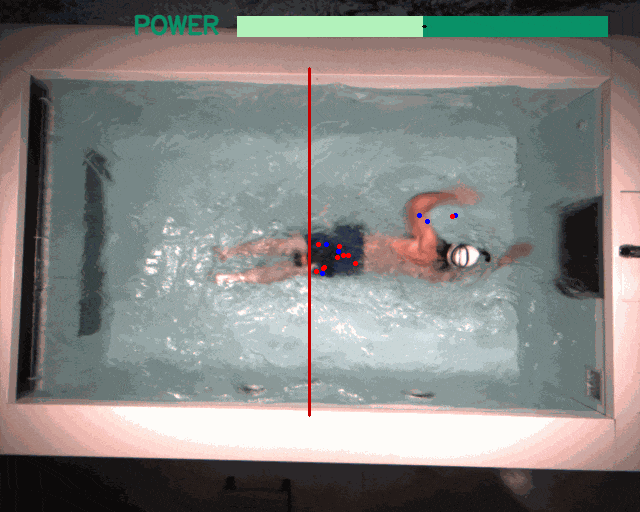
Applications beyond RL: The modular design and unified software pipeline of the framework have utility beyond reinforcement learning. We explored two such instances: interactive language-conditioned imitation learning (left) and classical control with deep learning based perception in a swimming pool environment (right).
Video
Engines
EAGERx enables a unified pipeline for real-world and simulated learning across various simulators. The following engines/simulators are already available for training and evaluation:
RealEngine for real-world experiments
PybulletEngine for PyBullet simulations
OdeEngine for simulations based on ordinary differential equations (ODEs)
Users can easily add their own engines by implementing the Engine interface.
Table of Contents
Cite EAGERx
If you are using EAGERx for your scientific publications, please cite:
@article{eagerx,
author = {van der Heijden, Bas and Luijkx, Jelle, and Ferranti, Laura and Kober, Jens and Babuska, Robert},
title = {EAGERx: Engine Agnostic Graph Environments for Robotics},
year = {2022},
publisher = {GitHub},
journal = {GitHub repository},
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/eager-dev/eagerx}}
}
Maintainers
EAGERx is currently maintained by Bas van der Heijden (@bheijden) and Jelle Luijkx (@jelledouwe).
How to contact us
For any question, send an e-mail to eagerx.dev@gmail.com.
Acknowledgements
EAGERx is funded by the OpenDR Horizon 2020 project.

